As a typical application of Mayr arc model which is best applicable to thermal mode phenomenon of a circuit-breaker, calculation of short-line-fault(SLF) breaking is introduced. Due to the very high rate of rise of the transient recovery voltage after the interruption of the current (current zero), a certain conductivity still exists between the contacts of a circuit-breaker, and the space can still be regarded as an arc for several ms.
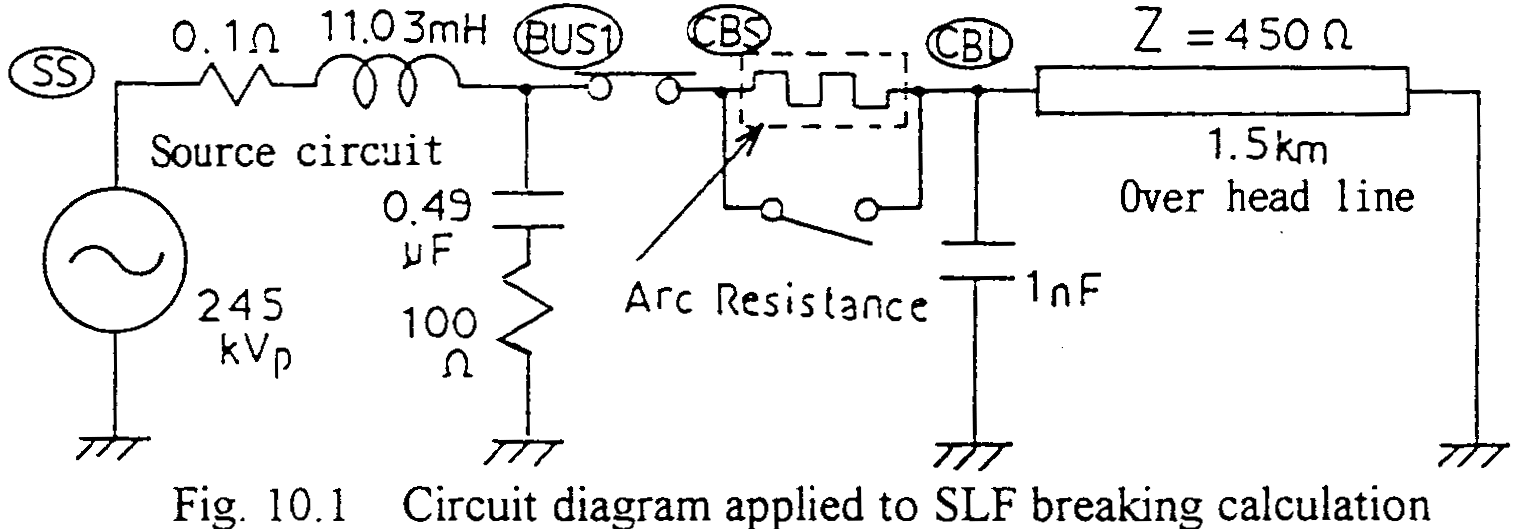
Fig. 10.1 shows a circuit diagram applied. For the purpose of this chapter, a simplified source side circuit is introduced, but the construction is widely applicable as an equivalent circuit seen from certain stations. The parameters of the line connected to the circuit-breaker are general values for an overhead transmission line. The line length 1.5km corresponds to the location of the grounding fault along the line.
For the purpose of more general application including the high current phenomena, Mayr and Cassie arc models connected in series are introduced in this case. But for the phenomena of short line fault breaking, only Mayr part is dominant, which can be certified by checking the arc resistance (or conductance) variations of both models.
The parameters in the calculation are:
-
N0=280000, and q=1.0E-6
-
G0=I2/N0
G=G0/(1+qs)